Zinc and selenium are two essential minerals that play a key role in the function of many enzymes. They also help protect against oxidative stress, which is caused by unbalanced levels of free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Zinc and selenium are both found in high amounts in animal foods like fish, meat, eggs and dairy products. However, they can also be found in plant foods like legumes and nuts.
Our bodies need a constant supply of these minerals to help regulate the immune system and maintain a strong metabolism. If you don’t get enough zinc or selenium from your diet, it can cause serious health problems.
Zinc deficiency is extremely common in the United States. In fact, at least one third of the population may be experiencing symptoms of zinc deficiency. Zinc is an essential trace mineral that plays a role in a wide range of biological functions.
Zinc and selenium are both found in meat, seafood and some plants. Other sources include whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds.
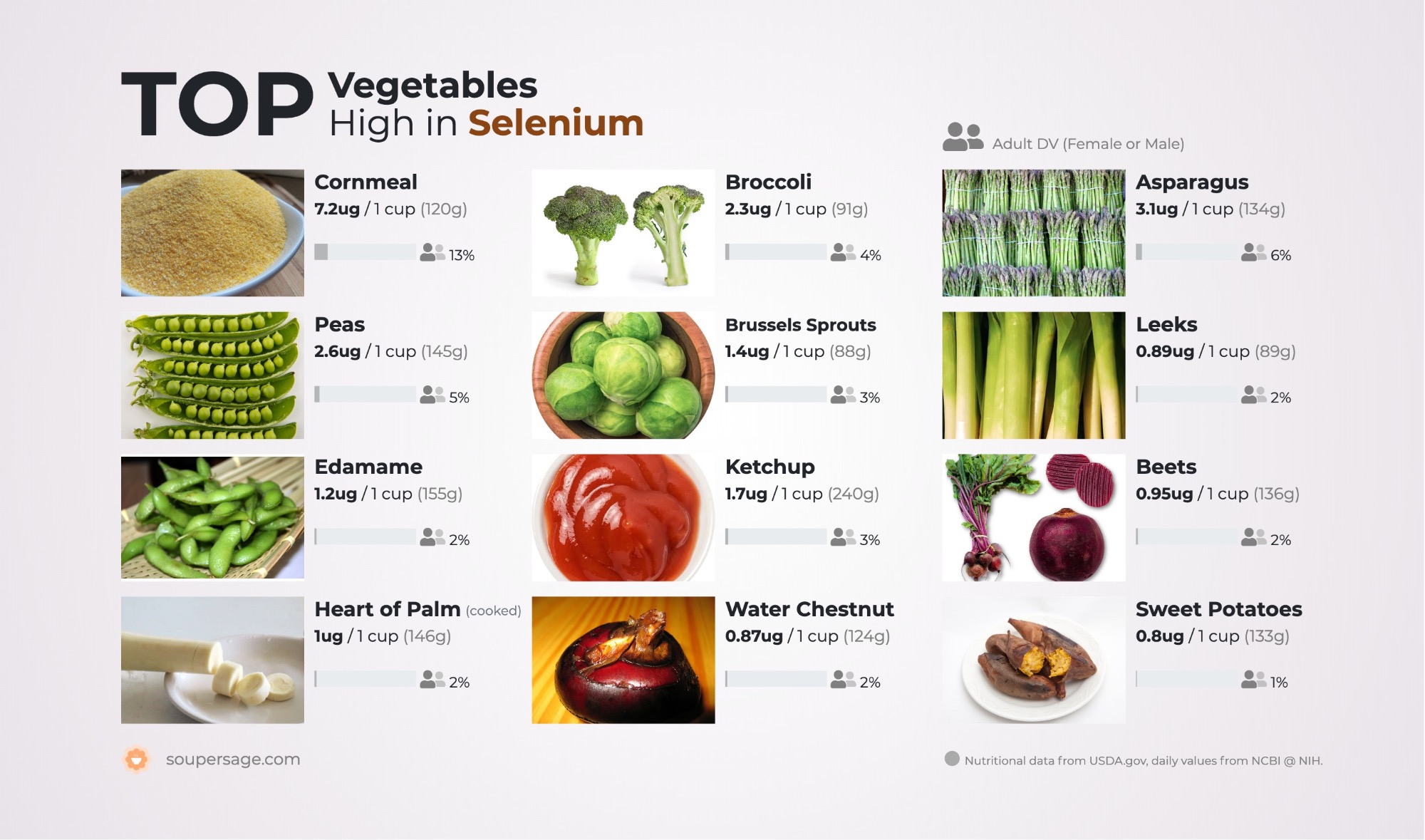
Selenium Rich Foods for Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition where your thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. Selenium is essential for normal thyroid function because it regulates hormone production. It also helps prevent oxidative damage to cells from free radicals in the body.
The best way to get more selenium into your body is by eating foods high in selenium such as walnuts, sunflower seeds and Brazil nuts. You can also take supplements if you do not like eating these foods regularly. The recommended daily dose is 55 micrograms per day for adults although some people may need more than this amount depending on their health status and other factors such as age or pregnancy status
The following is a list of the best sources of zinc and selenium.
Zinc Rich Foods
Zinc is an essential mineral that plays many roles in the human body. It is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions and helps maintain your immune system, skin, hair, nails, bones and more. A deficiency in zinc can lead to poor growth and development, impaired sense of taste or smell, poor wound healing, delayed sexual maturation in males and decreased fertility in females (1).
Foods high in zinc include:
Shellfish – Oysters contain the most zinc per serving with oyster extract providing up to 60 milligrams per tablespoon; followed by scallops at 14 mg per serving; clams at 12 mg per serving; mussels at 11 mg per serving; shrimp at 10 mg per serving; crab at 9 mg per serving; lobster at 8 mg per serving (2). Other seafood such as salmon, tuna fish and sardines are also good sources of zinc.
Meat – Beef contains between 3-8 milligrams per 3 oz serving cooked (3); poultry contains between 2-4 milligrams per 3 oz cooked serving (4); pork contains between 2-5
Zinc
Zinc deficiency is rare in Western countries, but can occur in people with malabsorption disorders, such as those with celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disease. Zinc deficiency can also occur in those who have had gastric bypass surgery.
Zinc is important for wound healing and immune function, which could explain why some studies have shown a link between zinc deficiency and low testosterone levels in men.
In one study, infertile men who received 75 mg of zinc per day for one year had an increase in sperm count and motility compared to those who did not receive zinc supplements.
Selenium
Selenium is an antioxidant mineral that helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Selenium deficiency can cause hypothyroidism, brittle hair and nails, muscle weakness and fatigue. Other symptoms of selenium deficiency include irritability and depression.
Severe selenium deficiencies are rare in the United States because most foods contain at least small amounts of selenium naturally. However, people living in areas where soil levels of selenium are low may be at risk for developing selenium deficiencies if they don’t eat foods high in selenium on a regular basis
Zinc is an essential mineral that is important for a wide range of biological processes in the body. Zinc deficiency can lead to malabsorption, immune system dysfunction, skin problems and poor wound healing.
Selenium is an essential trace element that helps regulate thyroid function and also functions as an antioxidant. Selenium deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of developing autoimmune thyroid disease, including Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease.
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for zinc is 11 milligrams per day for men and 8 milligrams per day for women. The RDA for selenium is 55 micrograms per day for adult men and women. Zinc and selenium deficiencies may result from malabsorption or poor nutrition. A nutrient-dense diet will help ensure adequate intake of these minerals.
Zinc is a mineral that plays a role in many of your body’s functions, including growth and development, wound healing, blood clotting, and immune system health. Low levels of zinc may cause symptoms such as loss of appetite, diarrhea, slow growth and delayed sexual maturation in children.
Selenium is a trace mineral found in soil, water and some foods. Selenium is an essential trace element that can help protect the body from oxidative damage. However, too much selenium can be toxic to your health.
Foods high in selenium include:
Brazil nuts
Beef liver
Oysters
Rice bran oil
Zinc and Selenium Benefits
Zinc is a mineral that plays an important role in the growth and development of your body. It also helps you maintain good health, fight infections, and build strong bones.
Selenium is a trace mineral that is important to your health. Your body needs selenium to produce antioxidants that help protect your cells from damage.
High levels of zinc and low levels of selenium can cause oxidative stress on the body, which can lead to inflammation and cell damage[1].
Zinc Rich Foods for Skin
Zinc is found in many foods like seafood, meat, legumes (beans), whole grains, nuts and seeds[2]. Zinc-rich foods should be included in a balanced diet because they contain other nutrients like protein or fiber which are good for you.
Here are some examples of foods rich in zinc:
Eggs [3] (1 egg has about 0.4 mg of zinc)

Beef liver (1 slice has about 0.8 mg)
Chicken breast (1 cup has about 0.6 mg)
Zinc and selenium are two nutrients that work together to help protect the body from oxidative stress.
Zinc is a mineral that plays an important role in the immune system, wound healing, and hormone regulation. Selenium helps convert vitamin C into its active forms. It also works with vitamin E to help prevent damage from free radicals.
Selenium-rich foods include asparagus, broccoli, garlic and onions. Zinc-rich foods include oysters, beef liver, nuts and beans.
Zinc is a mineral that is found in many foods, including meat, fish, poultry and whole grains. It’s also an essential mineral for your body.
Zinc is needed for proper growth and development during pregnancy and childhood. The mineral plays a key role in wound healing, cell division and blood clotting. Zinc also helps fight infection by boosting the immune system.
Selenium is a trace mineral that’s naturally present in soil and water across the globe. It’s also present in some foods, such as fish, meat, eggs and whole grains.
Selenium Benefits
Selenium is necessary for the proper functioning of many enzymes involved in thyroid hormone synthesis (1). These enzymes are called deiodinases, which convert inactive forms of thyroid hormone into active T3 and T4 hormones that can be used by cells (2). Selenium also supports normal growth and development during pregnancy and childhood (3).
Other studies show that selenium may help prevent oxidative damage from occurring within cells (4). Oxidative stress is caused by an imbalance between free radicals (unstable molecules) and antioxidants (molecules that protect against free radicals), which results in cellular damage or death (5). Antioxidants such as selenium help protect
Selenium is an essential trace mineral that plays an important role in thyroid health. Selenium-deficient diets have been linked to increased risk of autoimmune thyroid disease, including Hashimoto’s disease and Graves’ disease.
Selenium supplements are a common treatment for Hashimoto’s, but it is possible to get too much selenium. When you take too much selenium, it can cause gastrointestinal distress and other side effects.
Selenium Benefits for Hypothyroidism
Selenium is an essential trace mineral required by the body to convert T4 into T3, which is the active form of thyroid hormone. Selenium also helps support healthy immune function and antioxidant defense mechanisms in the body.
Selenium-rich foods include:
Brazil nuts (1 oz.)
Tuna (3 oz.)
Chicken liver (3 oz.)
Beef liver (3 oz.)
Selenium is a trace mineral that exists naturally in soil, plants and animals. It is found in some foods, such as Brazil nuts, tuna and organ meats. Selenium can also be taken as a supplement.
Selenium helps the body to produce antioxidants called selenoproteins. These protect the body from damage by free radicals, which are caused by environmental factors such as tobacco smoke or exposure to sunlight.
Free radicals damage cells and may contribute to conditions such as cancer and heart disease. Selenium may help prevent these diseases by acting as an antioxidant.
Selenium also plays an important role in thyroid hormone production — another antioxidant. The thyroid gland needs selenium to make thyroxine (T4), a hormone that regulates your metabolism by controlling how fast your body uses energy from food sources such as carbohydrates, fats and proteins.