Every cell in the body requires protein to do its job. Protein is used to make important parts of the body such as muscles, hair and skin. The food you eat contains protein, so you can get protein from the diet. Some foods that are rich sources of protein include lean meats, fish and poultry, eggs, nuts and seeds, tofu, cheese and yogurt.
Right here on Encycloall, you are privy to a litany of relevant information on proteins are made where in the cell, protein synthesis, protein function in cell, what produces proteins and so much more. Take out time to visit our catalog for more information on similar topic.
Produce protein for the cell

Proteins are made where in the cell?
Proteins are made in the ribosomes.
What is protein function in cell?
Proteins are involved in almost every biological process in cells. They can also be considered as the building blocks of life because they make up a large portion of our bodies. Proteins perform many functions such as: enzymes (molecules that speed up chemical reactions), antibodies (proteins that fight off foreign invaders), and hormones (signals that control how cells behave).

All cells need protein. The cell needs proteins for all its functions. Proteins are made where in the cell?
Proteins are made in the cytosol, within the ribosomes of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER).
What produces proteins?
Proteins are produced by ribosomes on the RER. They are then processed and transported to their destination where they perform their function.
Protein is the main structural material of your body. It is made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks for protein.
Protein is the most abundant substance in your body and makes up about 20 percent of your weight. Protein is necessary for growth, healing, maintenance and all other bodily functions.
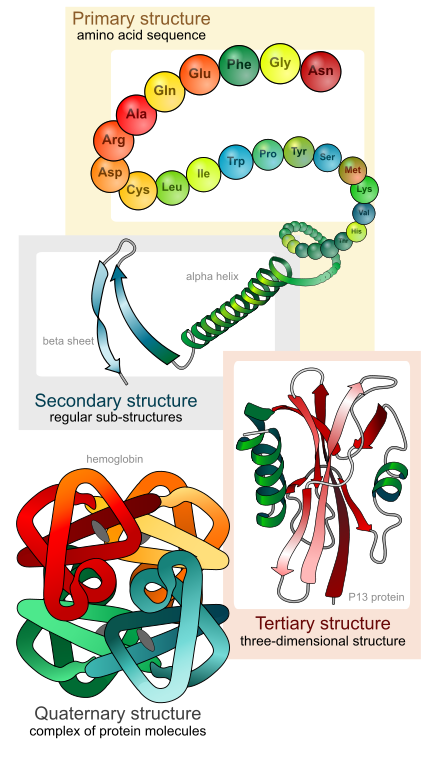
Amino acids are produced in cells by ribosomes, which are organelles found in all cells. Ribosomes make proteins by combining amino acids together in a specific order. The process that makes new proteins from existing ones is called translation.
Translation occurs when an mRNA molecule (messenger ribonucleic acid) travels out of the nucleus and attaches itself to a ribosome. Ribosomes then read each codon (a group of three nucleotides), one at a time, until they have read enough information to build a complete protein molecule.
Protein synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm of a cell.
Protein synthesis is the process by which genetic information stored in DNA is translated into proteins, through RNA transcription and protein translation. Protein synthesis typically consists of two stages: First, a specific amino acid chain tRNA molecule binds to the mRNA via an anticodon. The anticodon loops are complementary to the codon sequence of a specific codon, called an initiation codon (AUG). This initiates translation of a protein chain that will be linked to the tRNA molecule by peptide bond formation.

The process of protein synthesis takes place in the nucleus of the cell, which is why most proteins are synthesized in eukaryotic cells. RNA is also made in the nucleus, and so it’s not too much of a stretch to think that maybe some RNAs are also involved in protein synthesis. In fact, some of them are.
RNA molecules known as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are responsible for bringing amino acids to the ribosomes, where they can join together with other amino acids to form a chain that folds into a protein. Other types of RNAs have roles in regulating this process as well: messenger RNA (mRNA) carries information from DNA to ribosomes and signals stop codons; ribosomal RNA (rRNA) helps create ribosomes; and transfer RNA (tRNA) helps translate mRNA into proteins by bringing amino acids to the ribosome.