Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin, meaning that it dissolves in water. It is found in a wide variety of fruits and vegetables, including citrus fruits and juices, tomatoes, broccoli, and sweet peppers. Some foods are fortified with vitamin C.
Vitamin C plays an important role in the formation of collagen, which is essential for healthy skin, gums, bones, teeth and blood vessels. Vitamin C helps prevent scurvy — a disease associated with low levels of vitamin C — by helping your body absorb iron from foods like beans and leafy greens.
Vitamin C also helps boost your immune system and can aid in healing wounds more quickly.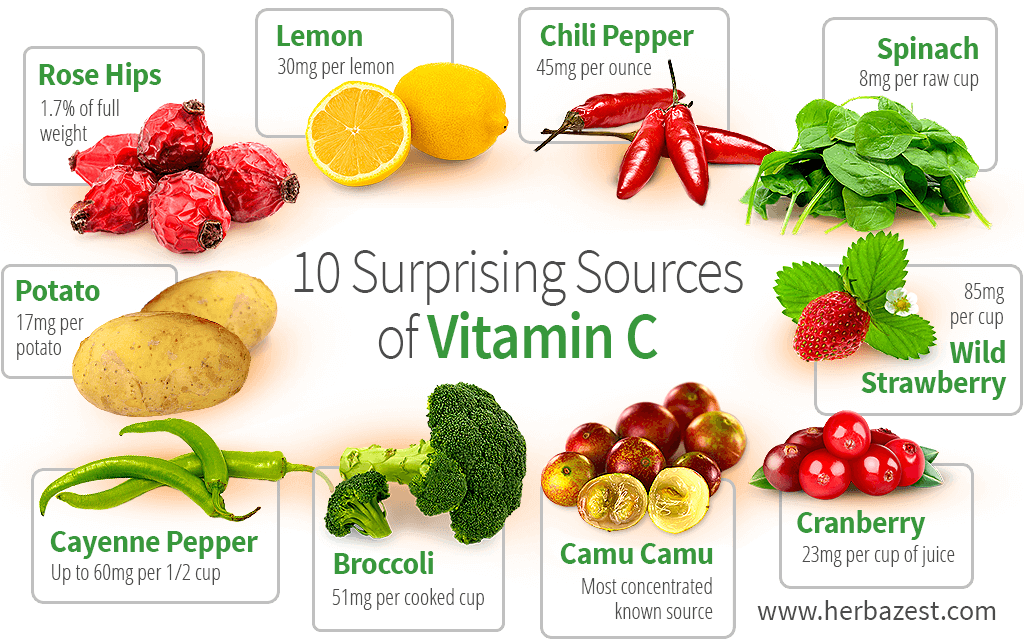
Vitamin C is essential for the growth and repair of body tissues. It helps your body absorb iron, aids wound healing and boosts immunity. The recommended daily intake of vitamin C is 75mg for adult women and 90mg per day for adult men.
Here are some vegetables that are high in vitamin C:
Arugula
Asparagus
Bell peppers
Broccoli
Brussels sprouts
Cabbage (red)
Carrots (orange)
Collard greens
These are the best sources of vitamin C, which is essential for a strong immune system, healthy skin and bones and more.
Strawberries: 1 cup has 110% of your daily value (DV) of vitamin C.
Oranges: 1 large orange has 103% DV of vitamin C.
Cantaloupe: 1/2 medium cantaloupe has 112% DV of vitamin C.
Guavas: 1 cup has 101% DV of vitamin C.
Kiwifruit: 1 medium kiwi has 66% DV of vitamin C.
High in Vitamin C
Vegetables high in vitamin C include:
Broccoli
Cauliflower
Cabbage
Kale
Spinach
Brussels sprouts
Citrus fruits (orange, grapefruit, lemon, lime) and berries (strawberry, raspberry, blueberry) are also good sources. The amount of vitamin C in these plants depends on the time of year they were picked. In general, the fresher the produce, the higher the vitamin C content.
Vitamin C is an essential nutrient that the body cannot produce on its own. It is found in many fruits and vegetables, and it is also added to some foods.

Vitamin C helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. It also promotes healing of wounds, assists in iron absorption and helps form collagen, which gives structure to blood vessels and other tissues.
Some people use vitamin C supplements to support their immune system during colds or other infections. However, there’s no evidence that taking vitamin C supplements can prevent colds or reduce the severity of symptoms.
The following lists show foods high in vitamin C:
Vitamin C is one of the most important nutrients for your body and is needed for numerous biological processes.
Vitamin C is an antioxidant and helps protect cells from damage by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable oxygen molecules that damage proteins, lipids (fats) and DNA.
Vitamin C also plays a role in collagen formation and acts as a cofactor in several enzymatic reactions involving amino acids, carnitine synthesis and dopamine metabolism.
Vitamin C is found in many fruits and vegetables, including citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons and grapefruits; kiwi fruit; papaya; strawberries; red peppers; broccoli; Brussels sprouts; cauliflower; kale; spinach; cabbage; watercress and tomatoes.
Vitamin K is a group of fat-soluble vitamins that play an important role in blood clotting, bone metabolism and cardiovascular health.
Vitamin K is synthesized from glucuronic acid, which is present in foods such as leafy greens, spinach, broccoli and Brussels sprouts.
Vitamin K deficiency can lead to bleeding problems. In addition, vitamin K may help protect against osteoporosis and heart disease by improving blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium) and improving calcium absorption in bones.
The following list of fruits and vegetables high in vitamin k coumadin includes:
Leafy greens such as kale, spinach, turnip greens and Swiss chard are good sources of vitamin K1 (phylloquinone). These vegetables are also good sources of other nutrients such as folate (folic acid) and vitamin C.

Broccoli contains moderate amounts of phytonutrients known as indoles. Indoles can help protect against certain cancers including breast cancer by blocking the growth of cancer cells. Broccoli also contains high levels of vitamin C which helps protect against the development of cataracts and age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Vegetables high in vitamin C
The following vegetables are high in vitamin C:
Kale (1 cup) – 133 mg
Spinach (1 cup) – 57 mg
Broccoli (1 cup) – 52 mg
Collard greens (1 cup) – 40 mg
Tomatoes (1 medium) – 32 mg
Brussels sprouts (1 cup) – 28 mg
Cabbage (1 cup) – 27 mg
Green pepper (1 cup) – 25 mg
The following is a list of fruits and vegetables high in vitamin C:

Red bell peppers
Broccoli
Cantaloupe
Kiwi fruit
Strawberries
Sweet potatoes (with skin)
Grapefruit (with peel)
Apricots
Oranges
Tomatoes
Vitamin K is a fat soluble vitamin that plays a role in blood clotting. It is used to treat vitamin K deficiency (vitamin K1), and to prevent bleeding or blood clotting problems after surgery (vitamin K2). Vitamin K can also be used to prevent blood clots in the veins of the legs, lungs, heart, and brain.
Foods high in vitamin K include:
Broccoli
Spinach
Brussels sprouts
Kale
Asparagus
Cabbage
Fruits and vegetables are a great way to get vitamins, minerals and antioxidants. They can also be a great source of fiber.
Vitamin K is one of the fat-soluble vitamins. It is found in leafy green vegetables like spinach, kale, broccoli and collard greens (1).
The vitamin appears to play an important role in bone health by helping to build strong bones and prevent fractures (2). In addition, it may help prevent cancer by preventing blood clots from forming in the arteries (3).
The best sources of vitamin K include:
Spinach
Broccoli
Kale.