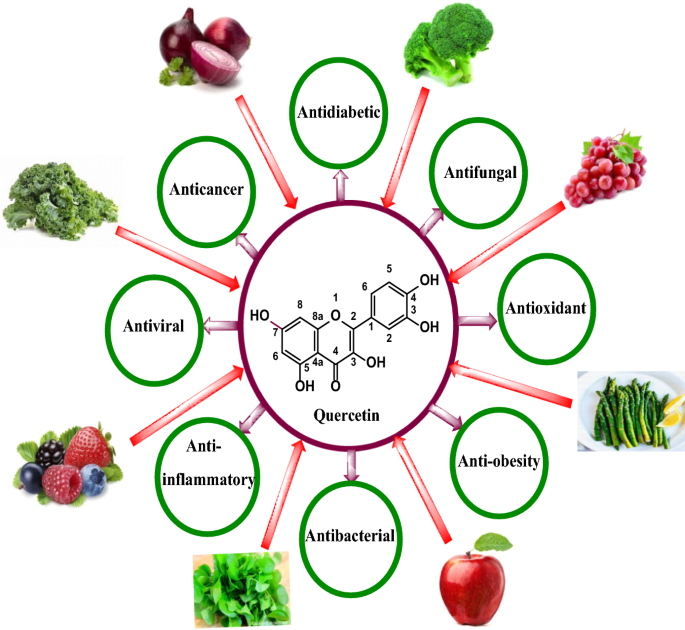
Quercetin is a flavonoid, a type of plant pigment found in many fruits, vegetables, leaves and grains. It is also called bioflavonoid. Quercetin occurs naturally in various foods, with onions and apples being among the richest sources.
Quercetin has antioxidant properties that may help prevent the development of diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD).
It may also help to protect against cancer.
The most common use of quercetin supplements is for allergies and inflammation.
Quercetin is a powerful antioxidant that is found in many plant foods, including fruits, vegetables, tea and wine. It has been associated with a number of health benefits, including the prevention of cancer, heart disease and inflammation.
This article lists some of the foods highest in quercetin, including green tea.
Foods High in Quercetin
Vegetables
Dark green vegetables are especially good sources of quercetin because they contain chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is what gives them their dark color and this pigment also helps protect these vegetables from damage by sunlight.
Some examples include:
Greens – broccoli, kale (curly), Swiss chard (silverbeet), spinach (English)
Brassicas – broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage (red), cauliflower
Legumes – green beans (French)
Quercetin is a natural antioxidant found in many plants. The best sources of quercetin are onions, leeks, broccoli, kale and apples. Quercetin has been shown to have many health benefits such as reducing inflammation and boosting immunity.
Quercetin is also used to treat asthma, allergies, congestion and hay fever. Quercetin supplements are available in tablet or capsule form.
How much quercetin should you take?
As a general rule, 500 mg of quercetin per day is recommended for most adults. However, if you have a medical condition such as asthma or allergies you may need more than 500 mg per day. If you are taking quercetin for heart disease or diabetes please check with your doctor before taking any supplements as there may be interactions with medication that could cause harm.
Quercetin is a bioflavonoid that’s commonly found in many foods, including red wine, onions, apples and citrus fruits. It’s also available as a dietary supplement.
Quercetin has antioxidant properties and has been suggested to have anti-inflammatory effects, although more research is needed to confirm these benefits.

The recommended daily intake (RDI) for quercetin is not established by the Food and Nutrition Board of the Institute of Medicine, but some experts suggest an intake between 40 milligrams and 400 milligrams per day depending on age and gender.
Foods containing quercetin include:
Onions
Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits)
Apples
Green tea
Quercetin is a naturally occurring chemical compound found in many plants. It belongs to the flavonoid group of polyphenols, which are plant-based chemicals that have been shown to have antioxidant properties.
Quercetin has been researched for its potential health benefits and is thought to be useful in preventing some chronic diseases. However, there is little evidence from clinical trials that it is effective for these conditions.
Quercetin supplements may be beneficial for people who suffer from allergies or asthma because they reduce histamine release from mast cells. This means that quercetin could potentially help to relieve symptoms of both conditions, such as sneezing, itchy eyes and runny nose.
In addition, quercetin appears to help treat hay fever by preventing the release of histamine during an allergic reaction and reducing inflammation caused by the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (messengers).
Quercetin supplements may also help prevent cancer by interfering with signal pathways involved in cell growth and survival. This means quercetin may slow down cancer cell growth and stop tumors from spreading around the body (metastasizing).
Quercetin is a natural compound found in fruits, vegetables, grains and other foods. It belongs to a family of plant pigments called flavonoids, which are known for their antioxidant properties.
Quercetin is one of the most popular flavonoids because it has been shown to have many health benefits. Quercetin has been studied for its ability to fight inflammation and prevent cancer. It may also help protect against heart disease and boost your immune system.
Quercetin is found in high amounts in apples, onions and tea. It’s also present in smaller amounts in berries, citrus fruits, broccoli and red wine.
Quercetin is a plant pigment that can be found in a wide range of fruits and vegetables. It is also one of the most common antioxidants in the Western diet, particularly when consumed through fruit and vegetable intake. Quercetin is a member of the flavonoid family, which has been shown to have both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Quercetin is found naturally in foods such as apples, onions, kale, broccoli, berries, red grapes and tea. The body uses quercetin to produce other antioxidants like resveratrol and catechins.
A bromelain supplement may help to reduce symptoms associated with allergies such as watery eyes and congestion. Bromelain helps break down proteins making it useful for reducing swelling associated with inflammation in the nose or sinuses (sinusitis).
Quercetin is an antioxidant flavonoid found in many fruits and vegetables such as apples, onions, berries and leafy greens. It has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects and may help reduce the risk of some cancers.
Quercetin is a plant pigment that gives fruits and vegetables their color. It’s also one of the most powerful antioxidants in the world, helping to protect your body from free radicals that can damage cells and lead to disease.
What Is Quercetin?
Quercetin is a type of flavonoid found in plants, most notably onions and apples. It’s a powerful antioxidant that helps prevent cell damage caused by free radicals — unstable molecules that can damage DNA if left unchecked. Quercetin also has anti-inflammatory properties and may help fight cancer development by inhibiting tumor growth or metastasis (the spread of cancer cells throughout the body).
How Much Quercetin Is in Foods?
The amount of quercetin in foods varies greatly depending on its concentration in the plant’s leaves or skin. For example, red onions have more quercetin than yellow ones because they’re exposed to sunlight while growing — which causes them to produce anthocyanins (a type
Quercetin is a flavonoid that is found in various plants and fruits.
The quercetin content of food products can vary considerably depending on the source of the food. The quercetin content of foods is usually expressed as quercetin equivalents (QE) based on the amount of quercetin that would be present if the food was extracted with water at pH 6.8.
The quercetin content in some common foods is shown below:
Food Quercetin QE**
Black tea 0.3-0.5 mg/L***

Red wine 0.5-1 mg/L***
Citrus fruits 0.2-0.3 mg/L***
Apples 0.4 mg/g fresh weight / 0.4-0.5 mg/g dry weight
Quercetin is a flavonoid, a type of antioxidant. It’s found in many fruits and vegetables, including apples, red onions, tea, red wine and berries.
Quercetin may help protect your skin against sun damage and aging. It may also help prevent cancer by stopping the growth of cancer cells.
Your body makes quercetin from other chemicals called phenolic compounds. Some foods have phenolic compounds that your body can use to make quercetin (1).
How much quercetin do you need?
The amount of quercetin you need depends on the condition you’re treating:
Preventing cancer — 20 to 30 milligrams per day (2)
Alzheimer’s disease — 100 milligrams per day (3)
Quercetin is a natural compound found in many fruits, vegetables, leaves and grains. It’s also a powerful antioxidant that may help increase immunity and decrease inflammation.
Quercetin is the most common flavonoid in the human diet, according to the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC). This phytonutrient is found in many fruits and vegetables, including apples, onions, tea and red wine. It’s also available as a supplement.
Quercetin is often used for:
Allergies
Arthritis
Asthma
Cancer prevention
Cholesterol reduction
Heart disease prevention.