The insoluble fiber in vegetables is low-digestible, meaning that it passes through the digestive tract without being digested. This type of fiber is found in raw fruits and vegetables, whole grains, nuts and seeds. Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water and therefore cannot be absorbed by the body.
Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like material that helps slow down digestion. Soluble fiber helps lower cholesterol, while insoluble fiber may help reduce constipation. Soluble fiber is found in oats, barley, legumes (beans and lentils) and psyllium seed husks.
Low Fiber Foods for Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy is a procedure used to examine the inside of the large intestine, or colon. The procedure may also be called a colon examination or a colonoscopy. During a colonoscopy, your doctor puts a lighted tube with a camera and tiny tools through your rectum and into your colon. This allows him or her to see and take tissue samples from your lower intestine.
If you are getting a colonoscopy, you might have been told that you need to eat low-fiber foods before the test. There are many reasons why this is done.
Here are some of them:
To make it easier for doctors to see inside your intestines during the exam
To allow doctors to take biopsies of any abnormal tissue they see during the exam (if necessary)
To help prevent cramping during the test
If you’ve been told to follow these guidelines, it’s important that you do so closely in order to ensure that everything goes smoothly during your exam.
Here’s a list of vegetables that are low in fiber:
Asparagus
Avocado
Bell Peppers (green, red, yellow)
Broccoli
Cauliflower
Mushrooms (white button)
Onions (red, white, sweet)
![]()
Low Fiber Vegetables
Vegetables are foods that are grown to be eaten. They can be eaten raw or cooked. Vegetables are low in fat and calories, and they are very good sources of vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients.
The most well-known vegetables include peas, green beans, carrots, potatoes, spinach and tomato. There are many other types of vegetables available including corn, cucumber, zucchini, okra and eggplant.
Some vegetables contain insoluble fiber while others contain soluble fiber. Insoluble fiber is the type of fiber that helps to prevent constipation because it adds bulk to stools by absorbing water from the colon walls as they move along through the intestines. This type of fiber does not dissolve in water but remains intact until it reaches the large intestine where it is then broken down by bacteria into short chain fatty acids which provide fuel for intestinal cells (1). Soluble fiber is known for its ability to lower blood cholesterol levels by binding with bile acids in the small intestines which prevents them from being reabsorbed (2).
Vegetables low in insoluble fiber include:
Asparagus (cooked) — 1.4 grams per serving
Broccoli (cooked) — 2.6 grams per serving
Brussels sprouts (cooked) — 2.9 grams per serving
Cauliflower (cooked) — 3.3 grams per serving
Green beans (cooked) — 3.7 grams per serving
Peas, dried — 7.8 grams per ¼ cup serving
many people find that adding fiber to their diet helps them feel full and satisfied.
Low-fiber foods are lower in fiber content than high-fiber foods. To find out which foods have the most fiber, see High-Fiber Diet: Top 25 Foods. Not all sources of fiber are created equal, however. Some types of fiber are better for your health than others.
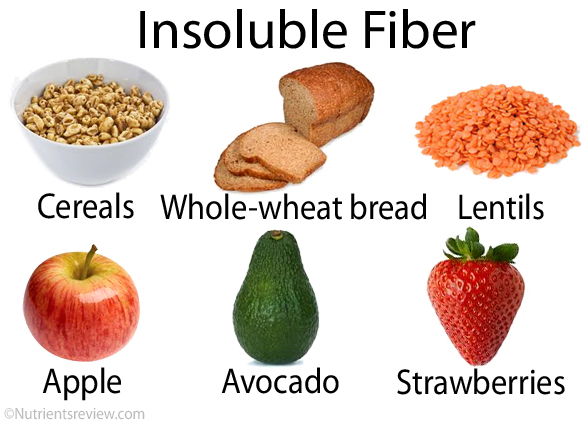
Insoluble Fiber

Insoluble fiber is found primarily in grains, seeds, and legumes. Insoluble fibers do not dissolve in water; they’re found in whole grains as well as brown rice, oatmeal, corn bran and wheat bran, nuts, seeds and legumes like beans, lentils and peas. Whole wheat bread has more insoluble fiber than white bread does because it contains the entire kernel of grain — bran and germ — rather than just the starchy endosperm (white part).
Soluble Fiber
Soluble fiber dissolves in water instead of just moving through your system intact as insoluble fibers do. Soluble fibers are found in high amounts in fruits such as apples, berries and pears; vegetables such as carrots and potatoes; legumes such as beans
Fiber is an essential nutrient that helps keep your digestive system healthy. But it’s not always easy to get enough of this nutrient. If you’re looking to add more fiber to your diet, try these low-fiber breakfast recipes. They’re simple, quick and delicious!
Breakfast is the most important meal of the day and should be included in any diet, whether you need to lose weight or simply want to stay healthy. The American Heart Association recommends eating a variety of foods throughout the day — including fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean protein sources — as part of a balanced diet. But just because something is healthy doesn’t necessarily mean it has high levels of fiber; some foods are naturally high in fiber while others have been fortified with added nutrients such as vitamins or minerals. What does this mean for you? It means that if you’re trying to increase your daily intake of high-fiber foods, it might take some trial and error before finding the right combination that works for you.
Low fiber breakfast is a great option for those who are suffering from constipation, diarrhea, or any other digestive problem. The low fiber breakfast is healthy and nutritious. It contains broken wheat, which is high in protein and iron content. This will help you to get your daily dose of calcium and vitamins.
Low fiber foods are good for the digestive system. They do not cause any harm to your body, as they go through digestion without causing any blockage in the intestine.
The following are some of the low-fiber foods that you can include in your breakfast:

Broken Wheat – Broken wheat is also known as bulgur wheat, which is made from whole wheat grains that have been steamed and then crushed into small granules. It has a nutty flavor, which makes it an ideal addition to soups and salads. You can add it to your breakfast cereal or make delicious pilaf with it by adding some spices like cumin seeds or turmeric powder.
Milk – Milk contains good amounts of calcium and vitamin D that help strengthen bones and teeth. You can add milk to your cereal or drink it plain as a snack between meals.
Eggs – Eggs are rich in proteins, which are essential for proper growth and development of children
Low fiber foods are a good option for people who have digestive problems such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or Crohn’s disease. They are also recommended for people who need to lower their risk of developing colon cancer.
Low fiber foods should be included in your diet if you have:
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). The high-fiber content of some foods can cause gas and bloating, which can worsen the symptoms of IBS. If you have IBS, talk to your doctor about gradually adding more low-fiber foods to your diet.
Crohn’s disease. A diet low in fiber can help reduce symptoms of Crohn’s disease because it helps decrease inflammation in the intestines — where inflammation is common in Crohn’s disease. However, it’s important not to eliminate all high-fiber foods from your diet when you have Crohn’s disease because eating too few high-fiber foods may increase your risk of developing kidney stones or osteoporosis. Your doctor may recommend that you take vitamin D supplements and calcium supplements to help prevent these conditions if you don’t eat enough calcium-rich dairy products or leafy green vegetables.
Colonosc
A low fiber diet is for people who have a bowel disease or are having surgery. It’s not for everyone.
A low fiber diet is a diet that contains less than 20 grams of fiber per day. Fiber is found in fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Fiber helps keep your digestive system healthy by moving food through your intestines at the right speed and in the right direction.
Some people may need to follow a low fiber diet before a colonoscopy or other medical test or procedure to prevent complications such as constipation and bowel blockages. A low fiber diet may also be recommended if you have certain digestive problems like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or Crohn’s disease, or if you have had problems with your intestinal tract during past tests or procedures.
If you need to follow a low fiber diet, talk with your doctor about how long you should be on this type of eating plan, what types of foods are allowed and whether there are any special instructions for you to follow while on such a diet.
Low Fiber Breakfast
Low fiber breakfast is a very important meal of the day. It helps to maintain your blood sugar levels, keeps you full for longer and prevents any spikes in blood sugar, which can lead to diabetes. Here are some suggestions for low fiber breakfast:
1. Low-Fiber Cereals
Low-fiber cereals are a good option if you are looking for low fiber breakfast. They have less than 1 gram per cup. Some examples include Corn Chex, Rice Chex and Wheat Chex. They also contain little sugar (less than 10 grams per serving).
2. Low-Fiber Breads
If you are looking for low fiber breads, you should try whole grain bread or whole wheat bread as they have more fiber compared to other types of breads such as white bread or rye bread. A slice of whole wheat bread has around 2 grams of fiber per serving while a slice of rye bread has around 1 gram of fiber per serving. If you want even less fiber in your diet then try high protein breads like Ezekiel 4:9 Sprouted Grain Bread which contains only 1 gram of fiber per serving but is rich in protein which helps reduce hunger pangs and keep you fuller for longer.