The type of SSL certificate you purchase will depend on the nature of your business and how much you plan to invest.
Domain Validated (DV) certificates are the most affordable option and are suitable for small businesses or personal websites. They’re also ideal for e-commerce sites that only accept payments through PayPal, Google Checkout or similar services.
A DV certificate is issued after a domain has been verified by a third-party authority, such as Comodo, Symantec or GeoTrust. The process involves verifying the registrant’s name and contact information, as well as confirming that the domain isn’t already in use by someone else. This process is easy for webmasters to complete and typically takes less than 24 hours for completion once all details have been submitted online.
Server Type For SSL Certificate
The 3 types of certificates are Server Certificates, Domain Validated (DV) Certificates and Organization Validated (OV) Certificates. The types of certificate awards are Domain Validation (DV), Organization Validation (OV) and Extended Validation (EV). The types of ssl certificate format are PEM and PKCS#12. The types of certificate authority are StartCom, Comodo, GoDaddy, GlobalSign and Thawte. There are 8 different types of SSL certificates available today: Domain Validation (DV), Organization Validation (OV), Extended Validation (EV), Wildcard SSL, Multi-Domain SSL, Secure Email Certificate, Code Signing Certificate and EV Code Signing Certificate.
There are three types of certificate awards:
Domain Validation (DV). It’s the cheapest type of SSL certificate, but it’s also the weakest one. The certificate authority only checks that you own the domain name you want to secure and that the domain is in good standing. If you’re planning on using a website for e-commerce or accepting credit cards, this isn’t an acceptable type of certificate.
Organization Validation (OV). This is a step up from DV and requires more validation of your company’s identity. The CA will do an online search and make sure your company exists, that there’s contact information for it, and that its address matches what was provided when you ordered the certificate. In addition, they’ll check with certain third parties — like Dun & Bradstreet — to verify your business’ legitimacy. Some CAs charge extra for this service.
Extended Validation (EV). EV certificates require all of OV plus additional verification at the CA level by asking questions about who owns a particular website when someone tries to visit it. They may ask for evidence that you own a domain name by sending them an email from an account associated with that domain, or they may ask for legal documents proving ownership over the domain
There are many types of SSL certificates, which you can use to protect your website’s traffic. The type of certificate you need depends on your business needs and budget.
There are three main types of SSL certificates:
Domain Validation (DV) Certificate — A domain validation certificate is the most basic form of SSL certificate available. It provides basic encryption for websites using HTTP connections only. This type of certificate does not provide any identity verification for the website owner. To purchase a DV certificate, you only need to provide the domain name for which it will be issued. Domain validation certificates typically cost less than other types of certificates because they are easier to obtain and do not require extensive vetting by third-party authorities like Symantec or Comodo Trust Network. However, they do not guarantee that the person who purchased them owns the website or has permission to use its content in any way.
Organization Validation (OV) Certificate — An OV certificate requires a higher level of identity verification than a DV certificate because it requires proof that the company requesting it is legally recognized as an organization within its jurisdiction. This means that in order to obtain an OV certificate, you must provide documentation proving that your business exists in some form outside of just being online.
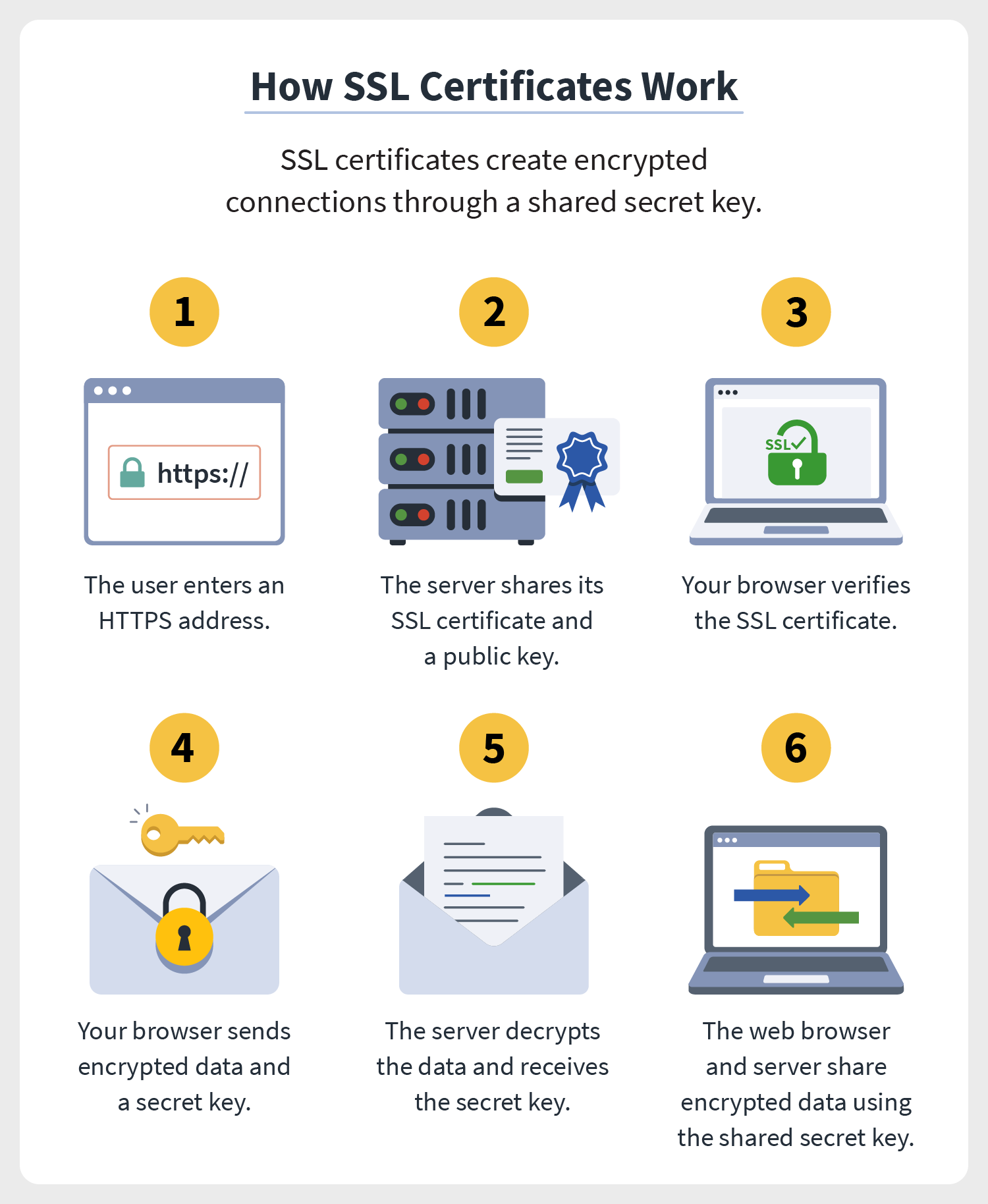
SSL certificates can be issued by a certificate authority (CA) or self-signed. The former is the most common and most secure option, while the latter can be used for internal applications and testing.
The three types of certificates include:
Domain Validation (DV) – This is the most basic type of certificate, where there is no need to verify who you are or your business. It’s good for websites that don’t require secure connections, but it doesn’t offer any real security benefits over a self-signed certificate.
Organization Validation (OV) – An OV certificate requires validation of your company’s identity before it can be issued. The CA will typically verify this information by contacting your company directly and asking for proof of ownership for your domain name(s). OV certificates are intended for companies who have a physical address or brick-and-mortar storefronts, so they can prove they own those domains without relying on third parties like GoDaddy or 1&1 IONOS.
Extended Validation (EV) – EV certificates require more extensive identity verification than OV certificates do. In addition to verifying that you own your domain name(s), an EV certificate also verifies that you’re operating as a legitimate business, not
The primary purpose of SSL certificate is for establishing secure connections between web browsers and web servers. It is also used to verify the identity of a person or an organization.
The most common types of SSL certificates are Domain Validated (DV) and Organization Validated (OV). Here are some other types of SSL certificates:
Wildcard Certificate: This type allows you to protect multiple subdomains with a single certificate. For example, if you want to protect all subdomains such as www.example.com, mail.example.com, ftp.example.com and so on, then you may use a wildcard certificate that can be issued with *.example.com as its domain name.
Multi-domain Certificate: With this kind of certificate, you can protect multiple domains at once by configuring them in your web browser settings. However, this type of certificate is more expensive than single-domain certificates because it requires additional validation steps during issuance process which includes obtaining identity information from each registered domain name holder individually before issuing the certificate for multiple domains at once.
Types of Certificate Awards:
1. Domain Validation (DV) SSL Certificates – These are the most basic type of SSL certificates. They are usually issued in minutes and cost $99 per year. DV SSL Certificates provide strong encryption and identity confirmation but do not verify the physical location of your organization or its legal existence.
2. Organization Validation (OV) SSL Certificates – OV SSL Certificates are more expensive than DV Certificates but they do verify your company’s physical address and legal existence. OV Certificates cost about $300 per year or more to obtain but they offer stronger encryption, better fraud protection and more trust from visitors who see your website address in their browser address bar.
3. Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates – EV SSL Certificates verify that you own and operate the domain listed on an EV certificate and that your organization is legally registered with a government authority like the Department of Commerce or Better Business Bureau (BBB). This kind of verification is done by performing an extensive background check on your business before issuing an EV Certificate which costs $500 per year or more depending on how much information you provide when applying for one
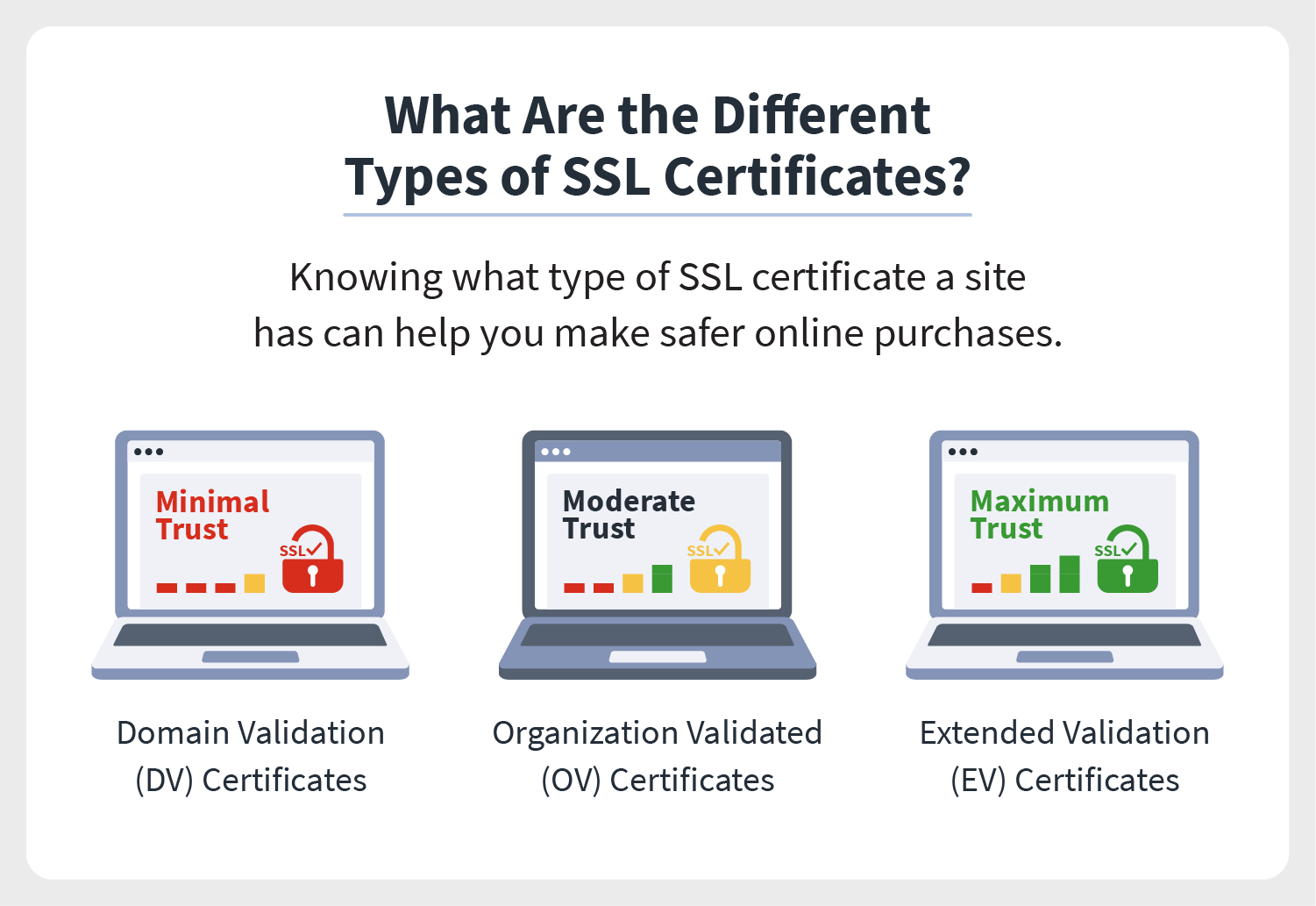
The three types of certificates are Domain Validation (DV), Organization Validation (OV), and Extended Validation (EV).
The DV certificate is the most affordable type of certificate and the only one that can be used to secure a website using HTTPS. It’s issued after a successful validation of information provided by the applicant, such as the domain name, physical address and contact information. The DV certificate is used by most small businesses and individuals who want to secure their websites with HTTPS.
The OV certificate is issued after a more thorough examination of applicant’s business history and identity. It’s often used by larger companies that want to secure their corporate websites or e-commerce sites with HTTPS.
The EV certificate is issued after an even more rigorous examination of business history, identity and technical capabilities. This type of certificate provides the highest level of trust among Internet users because it includes several security features that make it easy to identify phishing sites.
SSL Certificate Types
There are three types of certificates:
Domain Validation (DV)
Organization Validation (OV)
Extended Validation (EV)
There are several different types of SSL certificates available on the market, with varying levels of security.
There are three levels of certificates: Domain Validation (DV), Organization Validation (OV) and Extended Validation (EV).
Domain Validation certificates are issued to domains that have no special status or recognition. They are intended for personal use only, as there is no way for the issuing Certificate Authority to verify that the domain has been registered with a legitimate registrar. DV certificates are generally free and may be issued in just a few minutes.
Organization Validation certificates require proof that the applicant is an actual legal entity and have been registered with a recognized registrar. This typically requires submitting proof of incorporation documents or other government-issued ID information to an issuing CA. OV certificates tend to be more expensive than DV certs but they provide more validation and can be used on any subdomain within a domain name.
Extended Validation Certificates (EV) offer the highest level of identity verification available from any certificate authority today. EV certificates only display green address bars in browsers and require extensive due diligence before being issued by CAs like Comodo, Symantec and DigiCert.
The SSL Certificate Store offers free web hosting with a free
SSL certificates are used to encrypt data sent between your website and visitors’ web browsers. The three main types of SSL certificates are domain validation (DV), organization validation (OV), and extended validation (EV).
Domain Validation SSL Certificates
The most basic type of SSL certificate is a Domain Validation (DV) certificate. A DV certificate is typically issued within minutes, but it doesn’t verify that you’re a legitimate business. For example, it’s fairly common for hackers to purchase DV certificates to launch malicious phishing attacks.
Organization Validation SSL Certificates
An Organization Validation (OV) certificate goes a step further than DV by verifying the legal existence of your business. It may take several days or longer to issue an OV certificate, but they’re more secure than DV certificates because they require real-world proof of your company’s legitimacy — like proof of incorporation documents or an address verification letter from the post office or government agency.
Extended Validation SSL Certificates
A third type of SSL certificate is called Extended Validation (EV) and it’s the most secure option available because it requires an in-person meeting with someone at the issuing CA’s office in order for your identity.