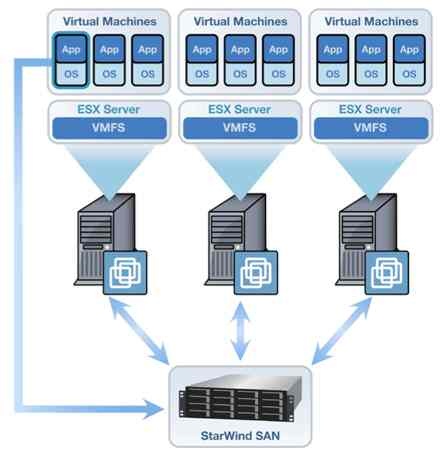
Server Virtualization is the process of running several virtual machines on one physical server. Server virtualization is an IT management technique that allows multiple operating systems to run on one physical server, which can reduce hardware costs and improve resource utilization.
With server virtualization, you can run multiple applications on a single physical server. This helps you reduce your total cost of ownership (TCO) because it allows you to consolidate multiple servers onto fewer servers, so you can reduce the amount of money spent on data center space, cooling and power. It also lets you use less physical hardware, which saves money on software licenses, maintenance and energy bills.

Server For Virtualization
Server virtualization is the process of using software to create one or more virtual machines (VMs) that run on one physical server. This allows you to run multiple operating systems on a single physical server, which helps reduce your hardware costs.
Each VM runs its own copy of an operating system and has its own virtual hard disk drive. Each VM also can use some or all of the hardware in the physical server, such as processor cores, RAM and storage space. The VMs share the other resources on the physical machine. For example, if one VM needs more disk space than what’s available in its virtual hard disk drive, it can use some of the free disk space on the host’s physical hard disk drive instead.
Server virtualization software is often referred to as hypervisor software because it creates a layer between your operating systems and hardware resources (such as CPUs and RAM). This layer lets you run multiple operating systems at once without interfering with each other’s performance or reliability — which would happen if you installed multiple copies of Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 side by side on one physical machine.
Hypervisors are available for many different types of servers, including x86-based PCs, mainframes and blades. There are also different types
Server virtualization is a method of consolidating multiple physical servers into one or more virtual machines. The result is that many servers can be run on a single host computer. This saves money and space by eliminating the need for multiple physical servers.
Server virtualization software allows you to run multiple operating systems on one physical machine. This saves space and money, as well as makes management easier.
The biggest benefit of server virtualization is that it allows companies to reclaim their IT infrastructure costs by reducing hardware requirements, which results in lower energy consumption and better efficiency.
Virtualization also improves disaster recovery (DR) capabilities because it allows you to migrate workloads between data centers without disrupting business operations.
Server virtualization has some drawbacks though: First, it requires specialized skills to manage VMs and perform routine maintenance tasks like patching and upgrading the operating system or application software running inside them. Second, while server virtualization can help you reduce your overall number of physical servers needed in the data center, it doesn’t address the need for additional network capacity between them (or between them and their clients).
Server virtualization is a technology used to run multiple operating systems on a single physical server. It allows an organization to consolidate multiple servers onto a single physical server. Server virtualization also makes it easier for IT administrators to deploy new applications, make software upgrades and perform maintenance without impacting production servers.
Virtualization is not just about cost savings. It also offers other benefits, including:
Easier management of resources: Virtualization makes it easier to manage multiple operating systems, patches and upgrades because they’re all running on one physical server. You can also create separate environments for testing purposes or as part of your disaster recovery plan.
Increased security: Virtual machines are isolated from each other, which minimizes the risk that one compromised application could infect others on the same computer. Plus, it’s easier to set up firewalls and intrusion detection systems to protect them from outside threats.
Flexibility: Virtual machines can be moved from one physical host to another without disrupting services or applications running inside them. This can be useful if you need more CPU power or storage space later on — just add another server and move the VMs over to it!
Server virtualization is a method of consolidating multiple servers onto a single physical server. This is done by placing each physical server in its own virtual machine, with all of the physical resources being shared by the VMs.
Virtualization reduces costs by allowing you to take advantage of economies of scale — instead of having a separate physical server for each application, you can use a single physical server to host multiple instances of those applications. That way, you can save money on hardware and electricity bills by using fewer servers overall.
Virtualization also makes it easier to maintain your applications and services because they’re all running on one system rather than many. You don’t have as many applications or services that need to be managed separately; instead, you just need to manage one instance of each application or service instead of many
When you virtualize a server, it’s still just as powerful as before — it just has fewer resources available to it than before
When you virtualize your servers, they’re no longer tied to one physical location because they’re running inside virtual machines
Virtualizing your servers makes them easier to manage because there are less things that need managing
You can allocate more resources per VM if necessary (such as more CPU cores)
Server virtualization is a technology that allows multiple operating systems to run on one server, instead of each operating system running on its own dedicated server.
This can be done in two ways:
Type 1 – Full virtualization: In this type of virtualization, the hypervisor (a software layer that runs between the hardware and the operating systems) creates a virtual machine that acts like a real computer. Each virtual machine has its own operating system and storage device, but they share the same processor and memory with other virtual machines. This is known as hardware-assisted virtualization because it uses special features in modern processors to split up resources among multiple users.
Type 2 – Paravirtualization: In this type of virtualization, the hypervisor creates an environment that is similar to how it would be if there were no hypervisor present at all. Only one operating system at a time can be installed in each virtual machine, but those operating systems can communicate directly with hardware devices instead of going through the hypervisor as they would if full virtualization were used.

Server virtualization software allows a single physical server to host multiple operating systems and applications. This is done by creating virtual machines (VMs) on top of the physical server. Each VM operates as if it were a separate computer, but in reality, they share resources with other VMs running on the same physical server.
1. Server Virtualization Software
Virtualization software is a type of software that allows multiple operating systems to run on the same physical server. This means that instead of having one server with all your applications installed, you can have multiple servers running different operating systems and applications. This allows you to save money on hardware, since you only need one physical server instead of multiple servers running separate operating systems.
2. Benefits Of Server Virtualization
There are many benefits to virtualizing your servers, including:
Lower costs – Running multiple operating systems on one physical server will lower your costs. You won’t have to buy as much hardware, or buy as powerful hardware, because you don’t need as much processing power for each application or operating system. You also won’t have to pay for licenses for each operating system that runs on each physical server. The savings add up quickly when you consider the cost of purchasing and maintaining multiple servers with different operating systems and applications installed on each one.
Easier management – Managing multiple physical servers can be difficult if they all need different updates applied at different times; this can cause downtime while waiting for updates to finish installing before being able to reboot again in order
Server virtualization is a form of computer virtualization that provides a single physical computing resource to multiple, isolated operating system environments (called “guests”) that can run their own applications on the host computing system.
Virtualization software allows the user to divide a single physical server into multiple virtual servers. These virtual servers act as if they were separate physical servers, although they share the same hardware resources.
Productivity – Server virtualization reduces the amount of time it takes to deploy new applications and services because you don’t have to spend hours configuring hardware and installing operating systems. This can significantly increase productivity.
Cost – Server virtualization helps businesses save money by reducing hardware costs and minimizing license fees for software such as operating systems and databases.
Reliability – Virtualized servers can be easily moved from one physical server to another without disrupting business activities or losing data. This makes them more reliable than traditional servers, which require downtime when moved between machines.
Server virtualization is a technique used to separate the software that runs on a physical computer into different, independent computing environments. Each of these virtual machines (VMs) can have its own operating system, storage and applications.
This approach allows organizations to consolidate multiple physical servers into one or more virtualized servers. In addition, it allows multiple VMs to run on a single physical server, which reduces hardware costs.
The main advantage of server virtualization is that it cuts down on the number of physical resources required to support computing needs. For example, if you have 20 servers running different applications, you might be able to convert them all into VMs and run them on one server.
Additionally, since each VM is isolated from other VMs running on the same machine, this approach also provides some level of security for your environment by limiting access between VMs and users who can only access their own VM. This could prevent a virus infection in one VM from spreading throughout your entire infrastructure or allow an attacker’s malicious code to affect only one VM instead of all of them at once.
Server virtualization is a great way to consolidate your servers, save money, and make your network more efficient. But there are some disadvantages that come with server virtualization as well.
The advantages of server virtualization include:
Reduced hardware costs. Since VMs share resources with other VMs running on the same physical server, there is less need for additional hardware to support your workloads. This means that you can use existing hardware more efficiently and reduce your overall IT budget requirements.
Improved resource utilization. With virtualization, you can maximize usage of resources such as processor cycles and memory — which means better performance for your applications and less chance of downtime caused by resource shortages.
Improved security from malware attacks. Virtualized servers are isolated from each other so that one compromised system does not have access to information stored on another system — even if it’s located on the same physical machine (host). This helps prevent sensitive data from being stolen or corrupted by an attack that’s focused on one VM rather than all VMs running on a host machine at once.
1. Consolidation of Servers
2. Flexible Management
3. Reduced Power and Cooling Costs
4. Increased Reliability
5. Virtual Machine Portability.