Being human means you will have some amount of stress which is fine because it is a part of life. When the level of stress becomes too high, it will affect your work, family and even your physical being. Relaxation is the key to deal with this creatures called stress. But relaxation is not easy right now that our lives are filled with thing that keep us going like paperwork, emails, social media, tv and other technology based activities. Taking care of yourself is also one such thing but how can we do it? What should we do? It’s simple human body needs protein to function properly, so when you exercise or do a specific activity make sure you eat the right foods like eggs, tuna and chicken to provide that additional energy and blood pressure. This is just one example; there are still things like antioxidants for health or vitamins for immunity or insulin for diabetes or extra-virgin olive oil for healthy fats and calories or probiotics for digestion problems that makes being a human easier.
Right here on Encycloall, you are privy to a litany of relevant information on proteins required for human body, protein benefits for human body, protein need for human body, protein food for human body and so much more. Take out time to visit our catalog for more information on similar topics.
Protein for human body
Protein is an essential nutrient for human body. Proteins are required for the growth and repair of body tissues. They are used to make hormones, enzymes, and antibodies. It is also used to maintain the body structure.
Protein helps in developing muscles, skin and hair. It also helps in repairing tissues damaged due to injuries or infections.
There are two types of proteins: complete proteins and incomplete proteins (or low-quality proteins). Complete proteins contain all the essential amino acids that the body needs but incomplete proteins do not have all the essential amino acids. Complete proteins can be obtained from animal sources such as meat, fish, poultry and eggs. Incomplete protein can be obtained from plant sources such as grains, beans and nuts.
The recommended dietary allowance for protein is 0.8 g/kg of body weight per day for adults aged 19-70 years old; however, it can vary based on your activity level and health status.
Adequate protein intake helps maintain muscle mass during weight loss diets or when you are ill or injured which increases your need for protein by up to 50%.
Proteins are essential for the human body. The human body needs protein to build and repair tissues, make hormones, enzymes and antibodies, and maintain a healthy immune system. Protein is also used to make new red blood cells.
In general, the body can make all the protein it needs from other substances in food. However, certain people may need extra protein, such as those with kidney disease or eating disorders.
Protein foods are meat, fish (including shellfish), poultry, milk and milk products, eggs, legumes (beans) and nuts. These foods contain all nine essential amino acids that your body cannot make itself but must get from food sources.
Protein is an essential nutrient for the human body. Proteins are needed for the growth and repair of body tissues. They are also used to make hormones, enzymes, antibodies and other body chemicals.
Protein food for human body
The amount of protein needed depends on age and sex. Protein is made of amino acids, which are small molecules that link together to form long chains. There are 20 different kinds of amino acids in the human body. Nine are considered “essential” because they cannot be produced by the body and must come from food sources such as meat, eggs, milk and nuts; the remaining 11 non-essential amino acids can be produced by your body from other substances.
Protein foods include:
meat (beef, pork)
fish (salmon, tuna)
eggs
dairy products (milk, cheese)
Protein is a macronutrient that we need to consume in order to survive. It provides the building blocks of our bodies and is necessary for growth, development, and maintenance of muscles, bones, cartilage, skin, and blood.
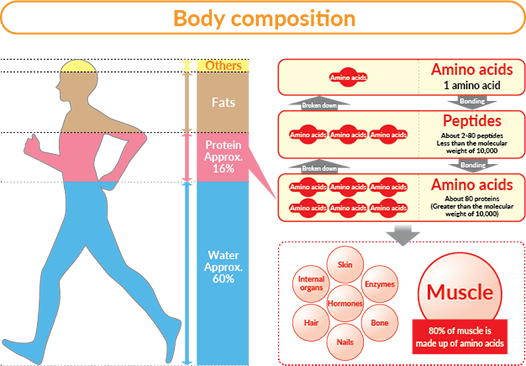
In fact, protein comprises about 15% to 16% of the total weight of our bodies. Thus it is not surprising that you have heard about protein many times. But what exactly does this nutrient do? What are its benefits? What foods should you eat to get enough protein? And how much do you need?

What is Protein?
Proteins are essential for the growth, maintenance and repair of all body tissues. They are also important in the functional maintenance of cells and the synthesis of hormones, enzymes and other compounds that are needed for growth.
Proteins are made up of chains of amino acids, which are linked together by peptide bonds. The amino acid composition of a protein determines its biochemical properties, including its solubility in water (hydrophilicity) and its ability to be denatured by heat or other agents (thermostability).
Proteins are a group of complex organic molecules. They are the main component of all living cells. Proteins are also essential for human body as they are required to maintain body structure, produce enzymes, hormones and other substances necessary for life.
The human body gets proteins from both food and from its own production inside the body. The proteins found in food include meat, fish, poultry, dairy products and eggs. Proteins are made up of amino acids (building blocks). There are 20 different types of amino acids that make up proteins in our bodies and these amino acids can be synthesized by our bodies from precursor molecules like glucose or fatty acids.
Proteins are the building blocks of the body. They form blood cells, muscles, skin, hair and even organs. The human body requires 20 amino acids in order to make its own proteins. These amino acids are found in foods that come from animals such as meat, fish and dairy products.
There are two types of protein: complete and incomplete. Complete proteins contain all of the essential amino acids that your body needs to function properly. Incomplete proteins lack some of those essential amino acids but can be combined with other incomplete proteins in order to create a complete protein source.
Protein helps maintain muscle mass and helps build new muscle tissue as well as repair existing tissue. It also helps you feel full longer after eating a meal so you don’t eat too much later on in the day or night which can lead to weight gain over time if not properly managed or monitored by your doctor or dietitian if necessary.

Eating enough protein is important for everyone but especially for athletes who need more protein than average people do just because their bodies are constantly breaking down muscle tissue through exercise which makes it easier for them to lose muscle mass than someone who does not exercise regularly at all or often
Protein is an essential nutrient that the human body cannot make on its own. It’s needed to build and repair tissues and cells, as well as enzymes, hormones and antibodies. The body uses protein to build muscle mass and to help maintain its normal function.
The average adult needs 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). This means that if you weigh 60 kilograms (132 pounds), you should eat about 48 grams of protein daily.
Protein can be found in a wide variety of foods, such as meat, fish, eggs and dairy products. However, there are also many plant-based sources of protein, such as soybeans, quinoa and legumes.
Proteins are the building blocks for the body’s tissues and organs. They are essential for growth, development and repair of all body parts. In fact, proteins make up more than half of our body weight.
The human body requires proteins for growth and repair of tissue, hormone production, enzyme activity, muscle contraction and many other important functions.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1145581060-c6f3afa5f308461cab0a77d79a51c68a.jpg)
Proteins are made up of amino acids linked together in a chain. There are 20 different amino acids that can be linked together to form a protein. The sequence in which these amino acids are linked determines which protein they will form. Some amino acids can only be produced by your body while others must be obtained from food sources such as animal tissue (meat), fish or eggs.
Proteins are the building blocks of your body. They are required for growth and repair of cells, tissues and organs.
There are 22 amino acids that combine to make proteins. Nine of these amino acids can be synthesized by the human body, while the remaining 13 must be obtained from food. Proteins are available in animal and plant sources; each type has its own unique composition of amino acids.
Proteins have many functions in your body, including building muscle mass, repairing damaged tissue and transporting oxygen in your blood. Proteins also serve as a source of energy for your body.
The amount of protein needed depends on age, gender and activity level:
Children need more protein than adults because their bodies are growing rapidly, but they don’t require more calories from fat or carbohydrate sources because they don’t need as much fuel for their activity level as adults do.
Pregnant women need about 75 grams of protein per day during their pregnancy (1). Protein is especially important for pregnant women because it helps build and maintain muscles needed for delivery (2). During breastfeeding, mothers should consume an additional 10 grams of protein per day to account for increased needs due to lactation (3).