A virtual private network (VPN) is a network that uses a public telecommunication infrastructure, such as the Internet, to provide remote offices or individual users with secure access to their organization’s network. The VPN allows employees to securely access their organization’s intranet while traveling outside the office, and it permits mobile users to securely access corporate applications while connected to a public Wi-Fi hotspot. To ensure security, the data transmission may be encrypted. A VPN is created by establishing a virtual point-to-point connection through the use of dedicated connections, virtual tunneling protocols, or traffic encryption. A VPN available from the public Internet can provide some of the benefits of a wide area network (WAN). From a user perspective, the resources available within the private network can be accessed remotely.
Vpn Server For Windows Server
VPN stands for virtual private network. A virtual private network (VPN) is a technology that creates a safe and encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the internet. VPN technology was developed as a way to allow remote users and branch offices to securely access corporate applications and other resources. It can also be used for mobile working, such as telecommuting. A VPN is created by establishing a virtual point-to-point connection through the use of dedicated connections, virtual tunneling protocols, or traffic encryption. A VPN available from the public Internet can provide some of the benefits of a wide area network (WAN). From a user perspective, the resources available within the private network can be accessed remotely.[1]
The most important thing to remember when setting up a Windows Server 2008 R2 or 2012 R2 or 2016 Server as a VPN gateway is that it needs to have a domain controller installed on it. This is one of two ways that you can install the Active Directory Certificate Services role on your server; either by installing it on an existing server or by creating an additional domain controller on one of these servers (or
Windows Server 2019 is the latest version of Microsoft’s server operating system. While it offers some notable improvements over previous versions, it still has some limitations when it comes to using VPNs.
Windows Server 2019 VPN Setup
Setting up a VPN on Windows Server 2019 requires you to install the Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) role. In this article, we’ll show you how to do this and how to configure it for use with your VPN provider.
Installing RRAS
To get started, open the Add or Remove Programs applet in Control Panel and click Add/Remove Windows Components. Scroll down until you see Routing and Remote Access Services and click its checkbox. Click Next and follow any prompts that appear on screen until the installation completes.
How to Configure VPN Server in Windows Server 2019?
If you want to configure VPN server on your Windows Server 2019, then you will need to install the Remote Access role. Once installed, you can configure a VPN connection. Here’s how:
1. Open Server Manager and click Tools > Add Roles and Features.
2. Click Next at the first page of the wizard, then select Role-based or feature-based installation and click Next again.
3. In the Features page, expand Remote Access and select Remote Access (VPN) if it’s not selected by default, then click Next twice until you reach the Confirmation page.
4. Review your choices and click Install to begin the installation process, which may take several minutes depending on your system’s configuration.
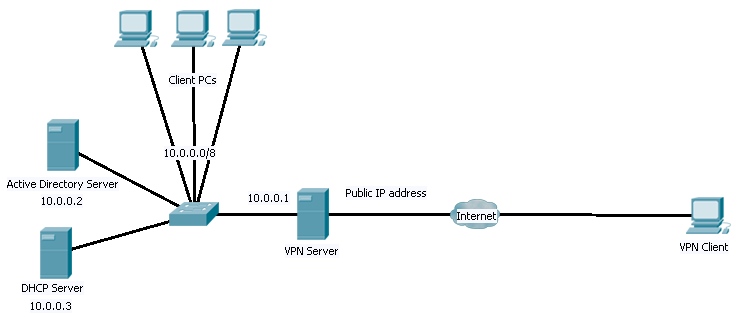
VPN server is a computer or a device that acts as a gateway or an intermediary between the computers that are part of the network and the Internet. In this way, these computers can communicate with each other and with users on the Internet. There are many types of VPN servers that you can use, depending on your needs and requirements. You can also choose from different operating systems such as Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2016.

The first version of Windows Server was released in 1993. It was a DOS-based operating system that had only a few features such as file and print sharing, email and messaging, and remote access. The latest version of Windows Server is Windows Server 2019, which was released in October 2018. It has many features that make it an ideal choice for businesses to use as a server.
Microsoft’s best-selling server operating system also comes with many built-in security features that protect against threats from the internet or on your network.
These include:
Hyper-V virtualization technology for running multiple operating systems on one physical machine
Windows Defender Antivirus software to protect against malware attacks
Azure Active Directory for identity management across cloud services
SQL Server for relational database management system (RDBMS) functionality
Windows Server 2019 is the latest version of Microsoft’s flagship server operating system. It was released on October 2, 2018, and includes improvements to security, performance and management. Windows Server 2019 has several new features that are relevant to IT professionals who need to implement a VPN server in their network environment.
Windows Server 2019 VPN Types
There are three different types of VPNs that connect devices together: site-to-site, clientless and split tunnel. These three different types are available on Windows Server 2019 and can be used in conjunction with each other or independently.
Site-to-Site VPN
A site-to-site VPN allows two or more remote networks to communicate securely over a public network such as the Internet. This type of connection is commonly used by companies that have branch offices located in different cities or countries. The company headquarters controls all of the information sent between offices by encrypting it before sending it across their secure network connections. Site-to-site VPNs provide both secure access for employees working remotely as well as secure connectivity for data transfers between sites within a corporate network environment
Windows Server is a server operating system developed by Microsoft. It is the most widely used server operating system in the world, and is estimated to run more than half of all websites in the Internet. It is available in three main editions: Windows Server, Windows Server Core and Nano Server; there are two main versions of each edition, named after the underlying hardware architecture: x86 and x64 (for IA-32 and x86-64 processors, respectively).
Windows Server includes a collection of services that provide core network identity and authentication functionality for network access servers. These services use Microsoft’s Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) to provide a directory service for network device authentication and authorization purposes.
The following table lists the components included in each edition of Windows Server:
VPN stands for “virtual private network”. It is a technology that allows you to connect your computer to another computer over the Internet. The main advantage of using VPNs is that they are encrypted and secure. A VPN makes it difficult for others to intercept and read your data.
There are many types of VPNs, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Here is an overview of some common types:
L2TP/IPSec – Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) or Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) used with IPsec encryption is one of the most common protocols used by corporate networks to provide remote access to employees. In addition to being relatively simple to set up, L2TP/IPSec can also be used on mobile devices such as tablets or smartphones running iOS or Android operating systems. The downside is that L2TP/IPSec can be slow because it requires multiple layers of authentication – typically two different passwords or keys – before reaching your device’s data stream.