You have to eat a healthy diet if you have diabetes. You know this, but what do you actually do it? I know: you googled ‘diabetes diet’. But the search results didn’t help. Very little useful information, tons of ads and ‘5 steps to diabetes freedom’ type posts that promise the earth but give very little in the way of actual specifics.
Right here on Encycloall, you are privy to a litany of relevant information on what can a diabetic eat for protein, what is good protein for a diabetic, what are high protein foods for diabetics, is a protein rich diet good for diabetics, and so much more. Take out time to visit our catalog for more information on similar topics.
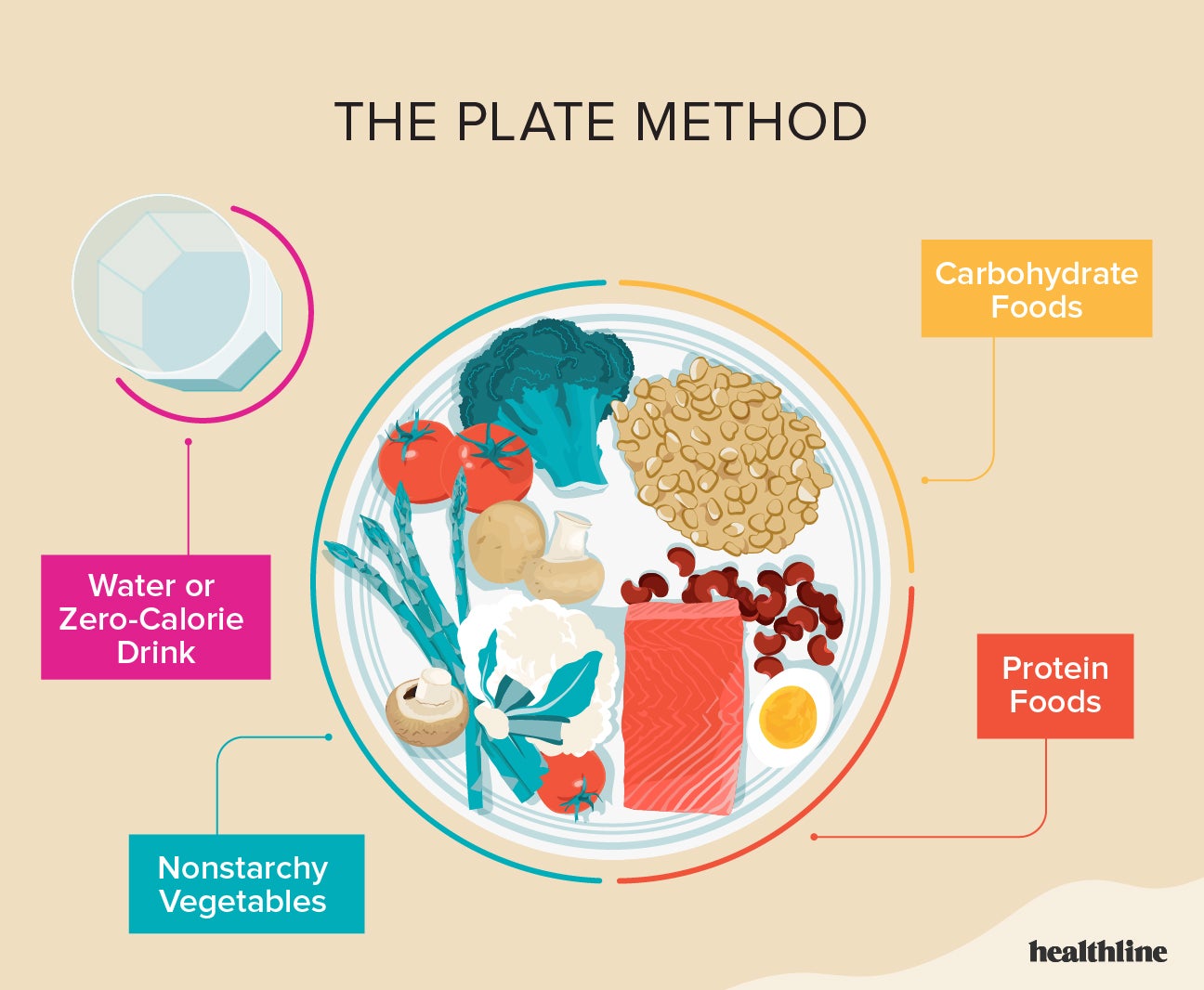
Protein foods good for diabetics
Protein is an essential nutrient for the human body, and a diet that contains sufficient protein helps you maintain your muscle mass and maintain a healthy weight. However, if you have diabetes, you need to be careful about how much protein you eat because excess protein may cause blood glucose levels to rise.
What can a diabetic eat for protein?
Protein is found in foods like meat, fish, poultry and dairy products like milk and cheese. These are also high-fat foods and should be consumed in moderation if you have diabetes.
What is good protein for a diabetic?
If you have diabetes, it’s best to consume lean meats or low-fat dairy products instead of fatty meats or full-fat dairy products. You should also avoid processed meats such as bacon and sausage because they contain added sugars or preservatives that can raise blood glucose levels.
What are high protein foods for diabetics?

Whole grains are another good source of protein that diabetics can eat regularly without worrying about causing a spike in their blood glucose levels. Some examples include brown rice, oatmeal and whole wheat breads.”
Diabetics should consume a diet that is low in fat, cholesterol and simple sugars. The following are some good sources of protein for diabetics:
Eggs. Eggs provide protein as well as vitamins A and D. They are also low in calories and fat.
Fish. Fish such as tuna, salmon and mackerel contain omega-3 fatty acids that reduce inflammation, improve heart health and help control blood sugar levels. Avoid fried fish because it contains more calories than baked or broiled fish.
Meat. Lean meats such as beef, lamb, veal and pork are all good sources of protein for diabetics. You can also use meat substitutes like tofu (bean curd) or tempeh (fermented soybeans). Both are low in fat and high in fiber, which helps lower cholesterol levels.
Protein foods are recommended for diabetics as they help to control blood sugar levels. Protein is an important nutrient that plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy body. It is important to eat sufficient protein in your diet as it helps to build muscles, repair cells and tissues, regulate hormones, make enzymes and hormones, transport substances within the body and maintain hair, skin and nails.
Protein Rich Foods for Diabetics:
Foods rich in protein include beans, eggs, low-fat dairy products, fish, poultry, lean meats like beef and pork loin chops or tenderloin steaks (2 oz cooked), soy products like tofu and tempeh (5 oz) etc.
Protein is an important nutrient for everyone, but it’s especially important for people with diabetes. Protein helps to control your blood glucose levels by helping to prevent high blood glucose levels after meals.
The amount of protein you need depends on your age and body size. The Institute of Medicine recommends that adults eat 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram (2.2 pounds) of body weight per day. If you have diabetes, you may need more than that to keep your blood sugar under control.
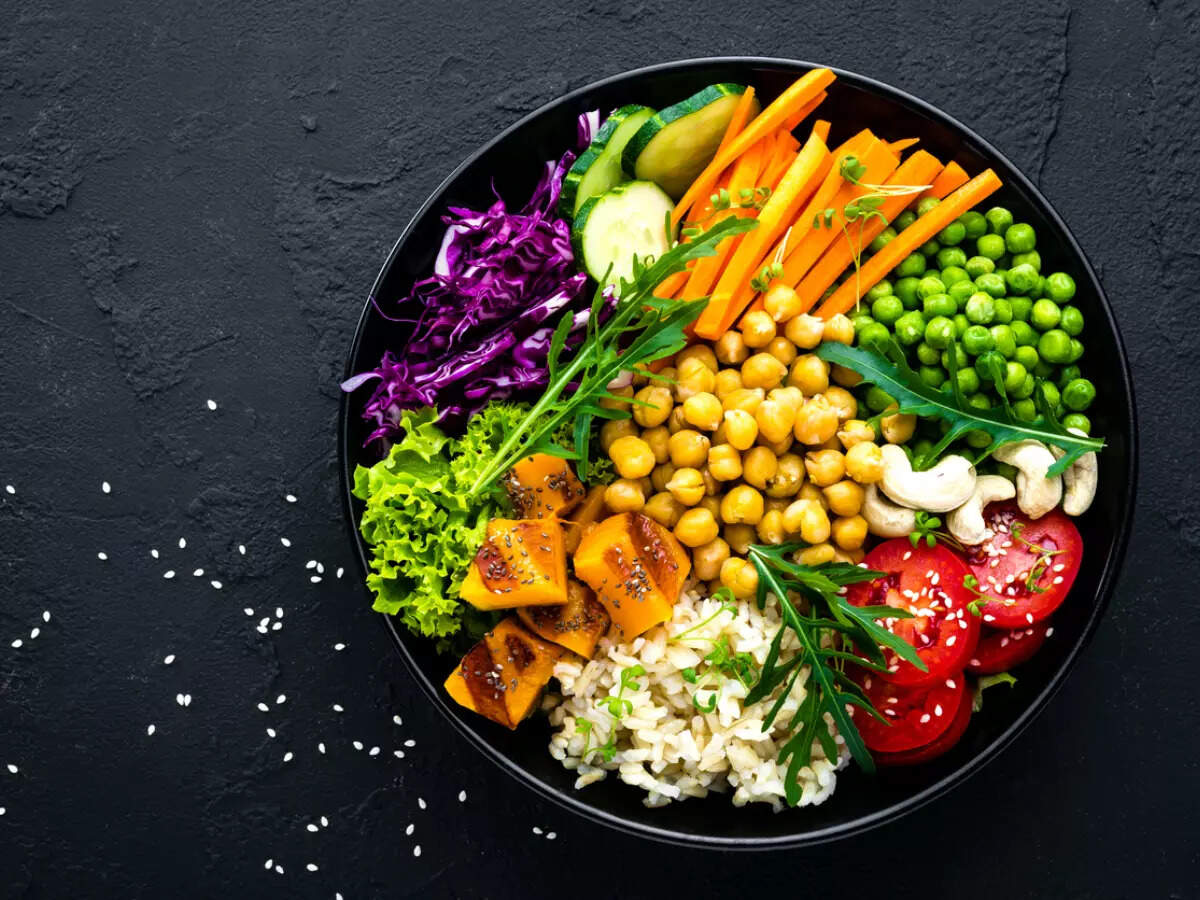

Diets high in protein can help control blood sugar levels, but they can also cause heartburn or diarrhea if they’re not managed properly.
High-protein foods include lean meats and poultry, seafood, legumes (beans), nuts and seeds — as long as they don’t contain too much fat or sodium (salt). Here are some examples:
Protein is a key part of a healthy diet. It helps you build and maintain muscle mass, which is important for staying active and maintaining a healthy weight. Protein also helps keep you feeling full longer and provides energy.
The recommended daily amount of protein is 0.8 grams per kilogram (2.2 pounds) of body weight per day, or about 50 grams for women and 65 grams for men. However, most Americans eat much more than that — an average of 150 grams per day — according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA).
Protein foods contain essential amino acids that your body needs but can’t make on its own, so they must be obtained from food sources such as meat, poultry, seafood and dairy products.*
Diabetes is a chronic disease that is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. According to the American Diabetes Association, diabetes affects approximately 29.1 million people or 9.4% of the population in the United States.
The following article will discuss various ways to improve your diet and lifestyle if you have diabetes or are at risk of getting it.
What Are High Protein Foods for Diabetics?
A high protein diet seems like a great idea for anyone who wants to lose weight or maintain their weight. However, many people who have diabetes are often told that they should eat a low-fat diet with lots of carbohydrates and sugars. This can be problematic if you’re trying to lose weight because it can make you feel hungry, which leads to overeating and feeling unsatisfied after meals — not exactly what you want when trying to lose weight!
It’s true that high protein diets can raise blood glucose levels more than other types of food. However, research has shown that this effect is only temporary — within several hours after eating a high-protein meal, blood glucose levels return to normal (or even lower than normal).
Diabetics are recommended to follow a low-sugar, high-protein and high-fiber diet. This helps to control blood glucose and cholesterol levels. The following foods provide good amounts of protein:
Lean beef, poultry, fish and shellfish.
Nuts and seeds.
Cheese.
Low-fat yogurt and milk.
Diabetics are more at risk of developing kidney disease, heart disease and stroke. Protein is essential for building and repairing muscle tissue, which can help maintain muscle mass and strength in people with diabetes.
Protein is also an important source of energy for the body. It contains the essential amino acids that your body needs to build proteins that make up your muscles, blood cells and many other parts of your body.
Protein-rich foods include:
Lean meat (beef, lamb, chicken)
Fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel)
Dairy products (milk and yoghurt)
Legumes (peas, beans and lentils)
Diabetes is a disease that can be managed. And the best way to manage it is through diet and exercise. But what should you eat?
Protein is an important part of a healthy diet, but it’s important to choose the right kind of protein.
Protein can help you lose weight, build muscle, and prevent diabetes — so what are the best sources?
High-protein foods for diabetics: Best options for weight loss

When you’re diabetic, you have higher blood sugar levels than normal. This can cause damage to your body over time because it places stress on your heart and kidneys. High blood sugar also increases your risk of developing certain other health conditions such as heart disease and kidney failure.
The good news is that there are plenty of ways to reduce your risk factors for these diseases by eating certain foods that keep your blood sugar levels in check. Here are some examples:
Protein is a vital nutrient for the body. It’s made up of amino acids, the building blocks of life. Protein is important for growth and development and it helps build and repair tissues in your body.
Protein is found in meat, fish, poultry, eggs and dairy products. Some plant sources contain protein such as legumes (beans), nuts, seeds and grains.
Diabetes management requires careful control of carbohydrate intake to reduce blood glucose levels, so you may need to limit your intake of high-carbohydrate foods such as pasta and bread. Healthy eating guidelines recommend eating at least 50g of carbohydrate per day for women and 65g per day for men – but only if this doesn’t increase your risk of hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar). If you have diabetes you should speak to your doctor or registered dietitian before making any changes to your diet.